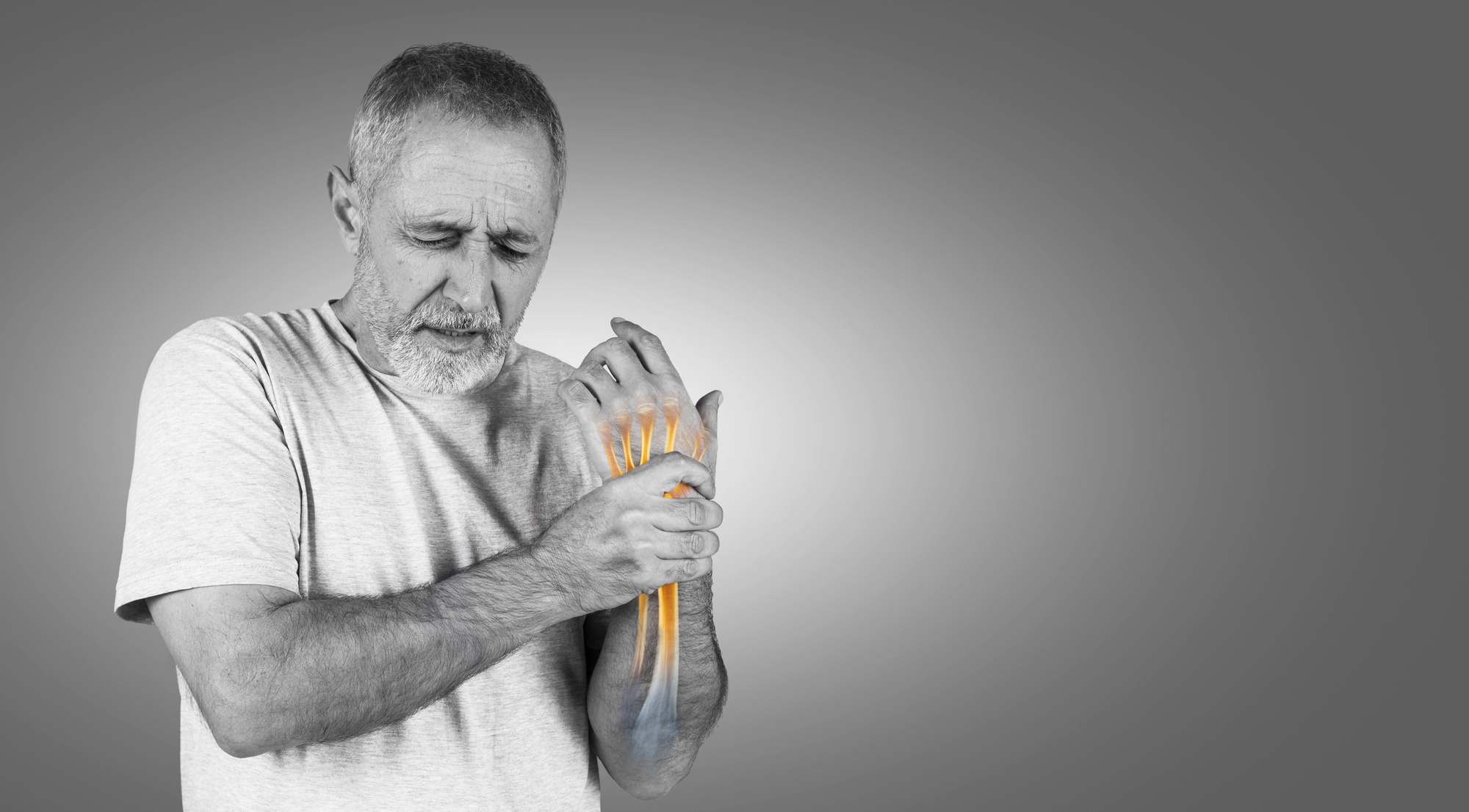
Unexplained bone pain can be more than a momentary discomfort, it can be a silent cry for help of your bones. Often overlooked, this symptom may indicate low bone density, a condition that compromises the strength of your bones and increases the risk of fractures. At Eastern Diagnostics, we emphasize the importance of early detection and proactive health management to maintain your bone health.
Understanding Low Bone Density
Bone density refers to the amount of bone mineral content in a specific area of your bones. Low bone density, also known as osteopenia, is a precursor to osteoporosis. In this condition, bones become weaker and are more prone to breaking under minimal stress. While osteopenia doesn’t always lead to osteoporosis, it is a warning sign that should not be ignored.
Connection Between Bone Pain and Low Bone Density
Bone pain, especially when persistent and unexplained, can be a red flag for low bone density. This type of pain is often dull and localized, typically worsening with weight-bearing activities. It may occur due to:
- Microfractures: Small cracks in weakened bones can cause pain even without significant trauma.
- Bone Remodelling: In individuals with low bone density, the natural process of bone regeneration may cause discomfort as bones struggle to repair themselves.
- Stress Injuries: Low-impact activities may result in stress fractures due to reduced bone strength.
Risk Factors for Low Bone Density
Several factors contribute to the development of low bone density. Understanding these can help identify individuals at higher risk:
- Age: Bone density naturally declines with age, particularly after 50.
- Gender: Women, especially postmenopausal women, are at greater risk due to hormonal changes.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition to osteoporosis can increase susceptibility.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a sedentary lifestyle negatively affect bone health.
- Dietary Deficiencies: Insufficient intake of calcium, vitamin D, and other nutrients critical for bone health.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic illnesses like rheumatoid arthritis, kidney disease, and hormonal disorders can lead to decreased bone density.
- Medications: Long-term use of corticosteroids and other drugs can weaken bones over time.
Diagnosing Low Bone Density
If you experience unexplained bone pain, a comprehensive diagnostic approach is essential. Early detection can prevent further complications. At Eastern Diagnostics, we use advanced imaging technologies such as:
- DEXA Scans (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry): This is the gold standard for measuring bone density. It provides precise data about your bone health.
- X-rays: Useful in detecting fractures caused by weakened bones.
- Blood Tests: These can identify deficiencies in calcium, vitamin D, and other markers of bone health.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Detecting low bone density early is crucial for several reasons:
- Prevention of Fractures: Early intervention can strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Tailored recommendations can improve bone health and overall well-being.
- Effective Treatment: Medications and supplements work best when initiated before severe bone loss occurs.
Managing Low Bone Density
Once diagnosed, managing low bone density involves a combination of lifestyle changes, nutritional support, and medical intervention:
- Dietary Improvements:
- Calcium-Rich Foods: Include dairy products, leafy greens, almonds, and fortified cereals.
- Vitamin D: Ensure adequate sunlight exposure or consider supplements.
- Protein: A balanced intake supports bone repair and maintenance.
- Exercise:
- Weight-Bearing Activities: Walking, jogging, and dancing help maintain bone density.
- Strength Training: Builds muscle and supports bone health.
- Medications:
- Bisphosphonates: Slow down bone loss.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Beneficial for postmenopausal women.
- Calcitonin and Parathyroid Hormone Therapy: Promote bone formation.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Ensure a healthy weight to reduce stress on bones.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Persistent bone pain, even if mild, should not be ignored. If you notice the following symptoms, consult a healthcare provider immediately:
- Pain that worsens over time or affects daily activities.
- A history of fractures with minimal or no trauma.
- Significant height loss or a stooped posture.
- Family history of osteoporosis or related conditions.
The Role of Regular Health Check-Ups
At Eastern Diagnostics, we advocate for regular health check-ups to monitor bone health, especially for individuals at higher risk. Periodic screenings allow for timely interventions and improved quality of life.
Unexplained bone pain is your body’s way of signaling an underlying issue. Ignoring it can lead to severe consequences like fractures and long-term disability. Understanding the link between bone pain and low bone density is the first step toward proactive care.
We are committed to providing state-of-the-art diagnostic services to help you take charge of your health. If you’re experiencing bone pain or have concerns about your bone health, don’t wait. Schedule an appointment today and let us help you build a strong foundation for a healthier future.
